- People-centered technology for a sustainable future
- The path for an effective impact
- The potential of design in knowledge transfer process
- Knowledge transfer between professionals
- Knowledge sharing for citizens
- Knowledge sharing for kids
- Knowledge sharing in COREu project through C4Learn
- C4Learn for citizens
- C4Learn for kids
- Conclusions
People-centered technology for a sustainable future
Engaging with people-centered technology is crucial for fostering real connections and driving adoption. By designing with empathy, we ensure that digital tools resonate with users, enhancing both satisfaction and trust. This approach is key to building sustainable, smart environments that truly meet the needs of our communities.
At the recent Sustainable Places 2024 conference, the COREu project was presented by Caterina Calefato, EU project division lead for Domina NextDomina Next, focusing on the importance of knowledge transfer in building awareness and social acceptance of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS).
The path for an effective impact
From the Built4People Stakeholders Forum to the Sustainable Places Conference 2024, the focus remains on the European Green Deal, with housing as a major priority and a strong emphasis on implementing its objectives. The building sector, responsible for over 30% of CO₂ emissions, is seeing significant improvements, but much more is needed at a faster pace. As a significant CO₂ emitter, the building sector is a relevant stakeholder for CCS technology and the COREu project .
Building next-generation built environments requires considering the positive and negative impacts of digital technologies and solutions. Multidisciplinary and multi-actor approaches are essential to create lasting impacts beyond project boundaries. Design serves as a crucial component of the methodological toolbox for creating sustainable cities, smart solutions, and AI-powered systems. By integrating human-centric design principles, iterative processes, and interdisciplinary collaboration, design ensures that technological advancements meet the needs of users. By focusing on human-centric design, we can create more intuitive, accessible, and effective technologies that enhance user experience and drive greater adoption. This approach not only supports the goals of sustainability and smart environments but also ensures that technological advancements are inclusive and beneficial to all members of society.
The potential of design in knowledge transfer process
Knowledge transfer is also a matter of design, specifically content design. Hence, knowledge transfer about CCS technologies should not only be informative but also help users understand and emotionally connect with the technology. With the EU’s population of approximately 447 million people, where just a small percentage are domain-related technicians, we need to gather to different audiences and provide knowledge transfer that is people-centric, respecting their needs: professionals, citizens and kids.
Knowledge transfer between professionals
Professionals need access to the innovative aspects of the COREu project and the technical advancements in CCS to understand the project’s significance and potential impact.
Knowledge sharing for citizens
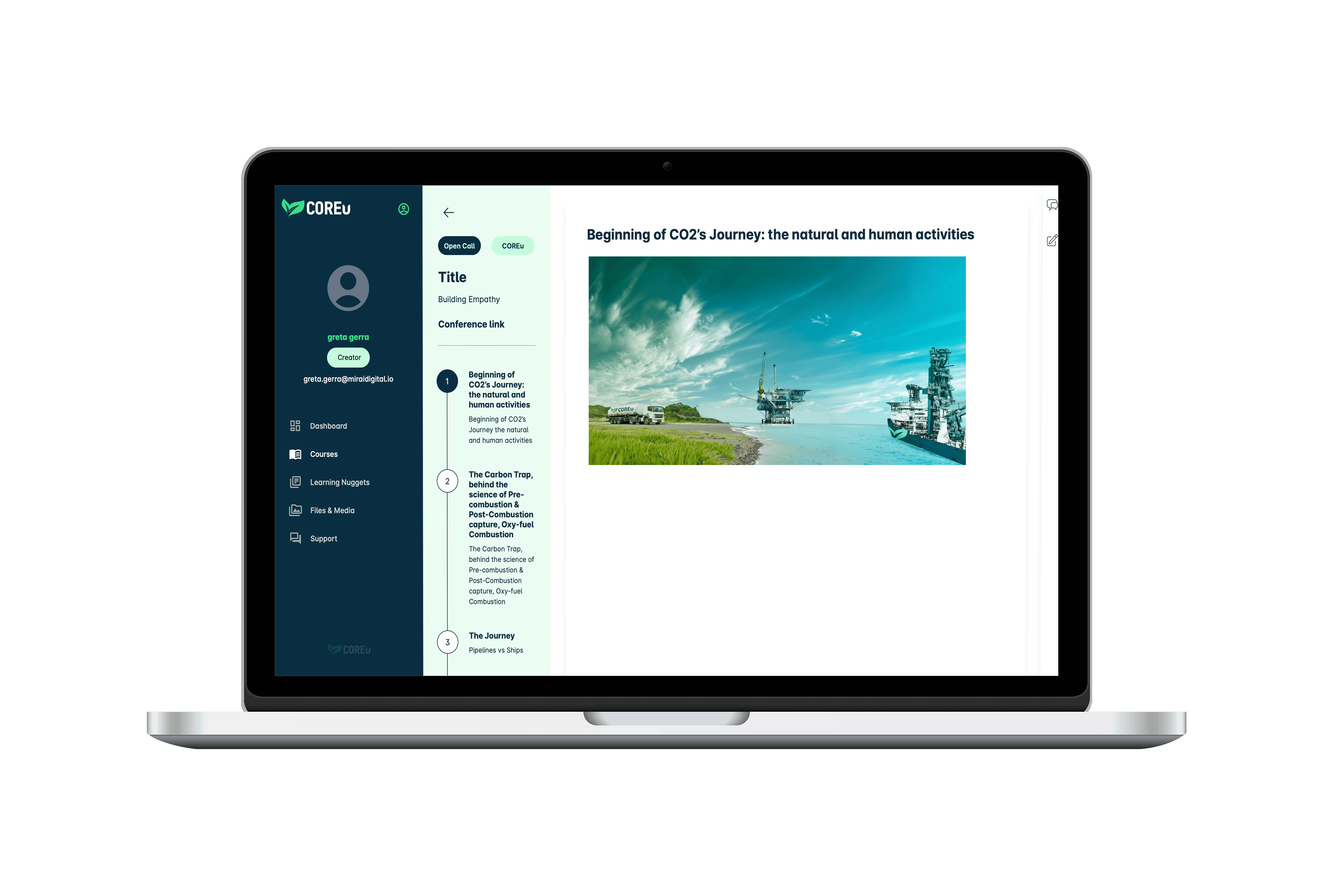
Citizens need to build a connection with the technology. By focusing on CO₂ as a journey, the concept becomes more relatable, helping people see the practical benefits of CCS in reducing emissions and combating climate change.
Knowledge sharing for kids
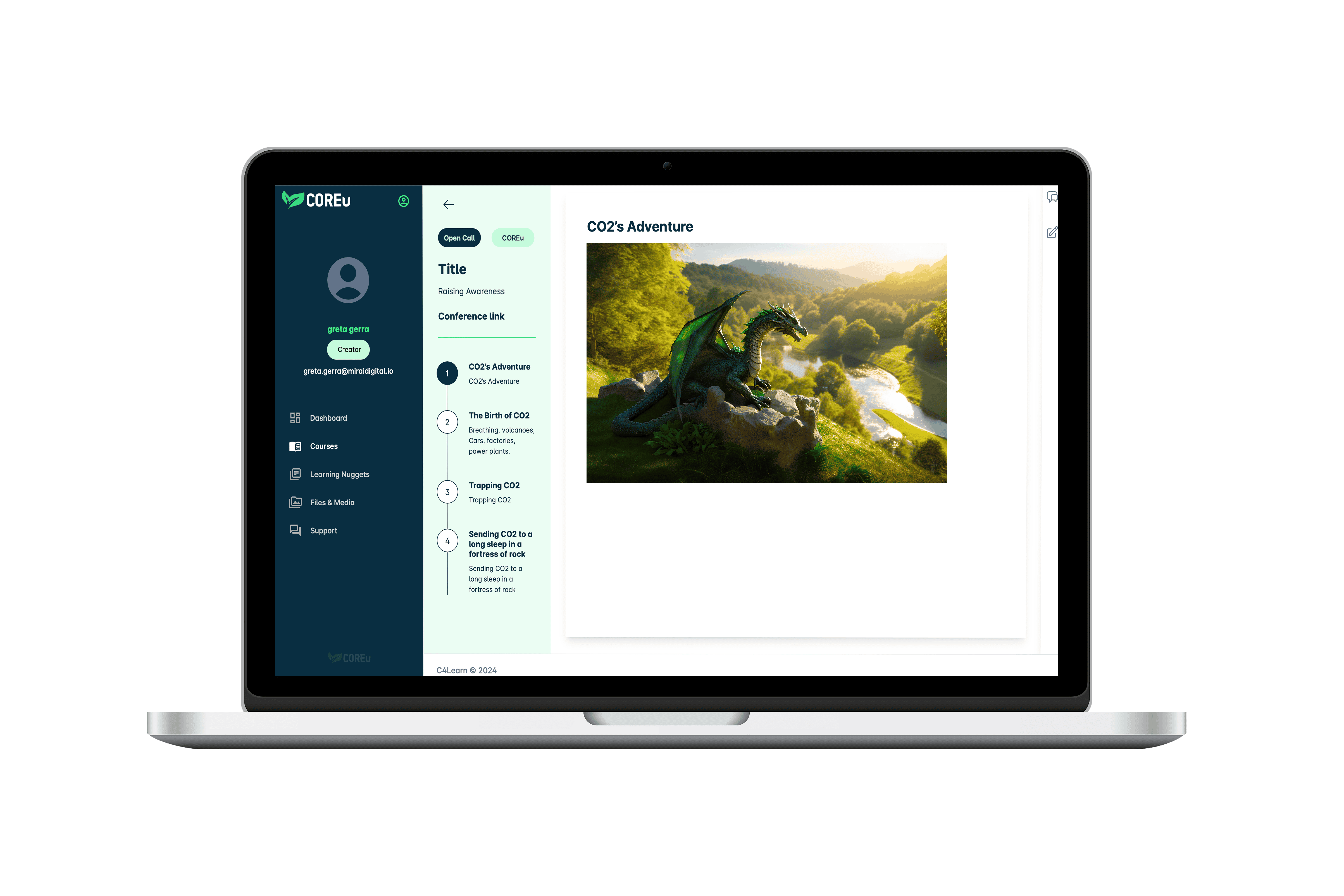
Kids need to become responsible citizens and mindful of the impact of human life on the environment. Presenting CCS as a CO₂ adventure engages young minds and sparks their interest in environmental science and sustainability.
Knowledge sharing in COREu project through C4Learn
In COREu, we utilize the Coreu4Learn LMS to manage content tailored for diverse audiences, emphasizing both empathetic design and scientific rigor.
For each audience we have customized different courses with the correct tone of voice:
- For professionals we have developed a course that can encourage them to take action by supporting and investing in CCS initiatives; this course is divided into 4 chapters:
- Chapter 1: The Birth of CO2: the natural and anthropogenic sources.
- Chapter 2: The Capture Phase: Pre-combustion & Post-Combustion capture, Oxy-fuel Combustion.
- Chapter 3: The Transport Phase: Pipelines vs Ships.
- Chapter 4: The Storage Phase: Geological, Ocean and Mineral Storage.
C4Learn for citizens
For citizens we have created a course that builds empathy and helps people understand the challenges and efforts involved in capturing and storing CO₂; this course is divided into 4 chapters:
- Chapter 1: Beginning of CO2’s Journey the natural and human activities.
- Chapter 2: The Carbon Trap, behind the science of Pre-combustion & Post-Combustion capture, Oxy-fuel Combustion.
- Chapter 3: The Journey: Pipelines vs Ships.
- Chapter 4: The Final Destination: Geological, Ocean and Mineral Storage.
C4Learn for kids
Finally for kids we have created a course to start raising awareness of the issue by teaching them the importance of CCS technologies in mitigating climate change; this course is divided into 4 chapters:
- Chapter 1: CO2’s Adventure.
- Chapter 2: The Birth of CO2: Breathing, volcanoes, Cars, factories, power plants.
- Chapter 3: Trapping CO2.
- Chapter 4: Sending CO2 to a long sleep in a fortress of rock.
Conclusions
The commitment to conveying knowledge using a digital tool on a topic like CCS is significant and not free of challenges. To facilitate the process and achieve the desired results, it is essential to design communication that remains close to citizens' needs and listens to their feedback in a virtuous cycle generated by information sharing.
Staying up-to-date with the COREu project and its developments is easy; just follow the following LinkedIn pages at these links
> Domina Next LinkedIn page
> COREu LinkedIn page